Recall 1:
Case of SLE, arthritis, and malar rash – What is the most appropriate treatment?
A) Hydroxychloroquine plus analgesics ✔️
Recall 2:
What is the most common presentation in SLE?
A) Malar rash
B) Polyarthritis
C) Seizure
D) Arthritis ✔️
Recall 3:
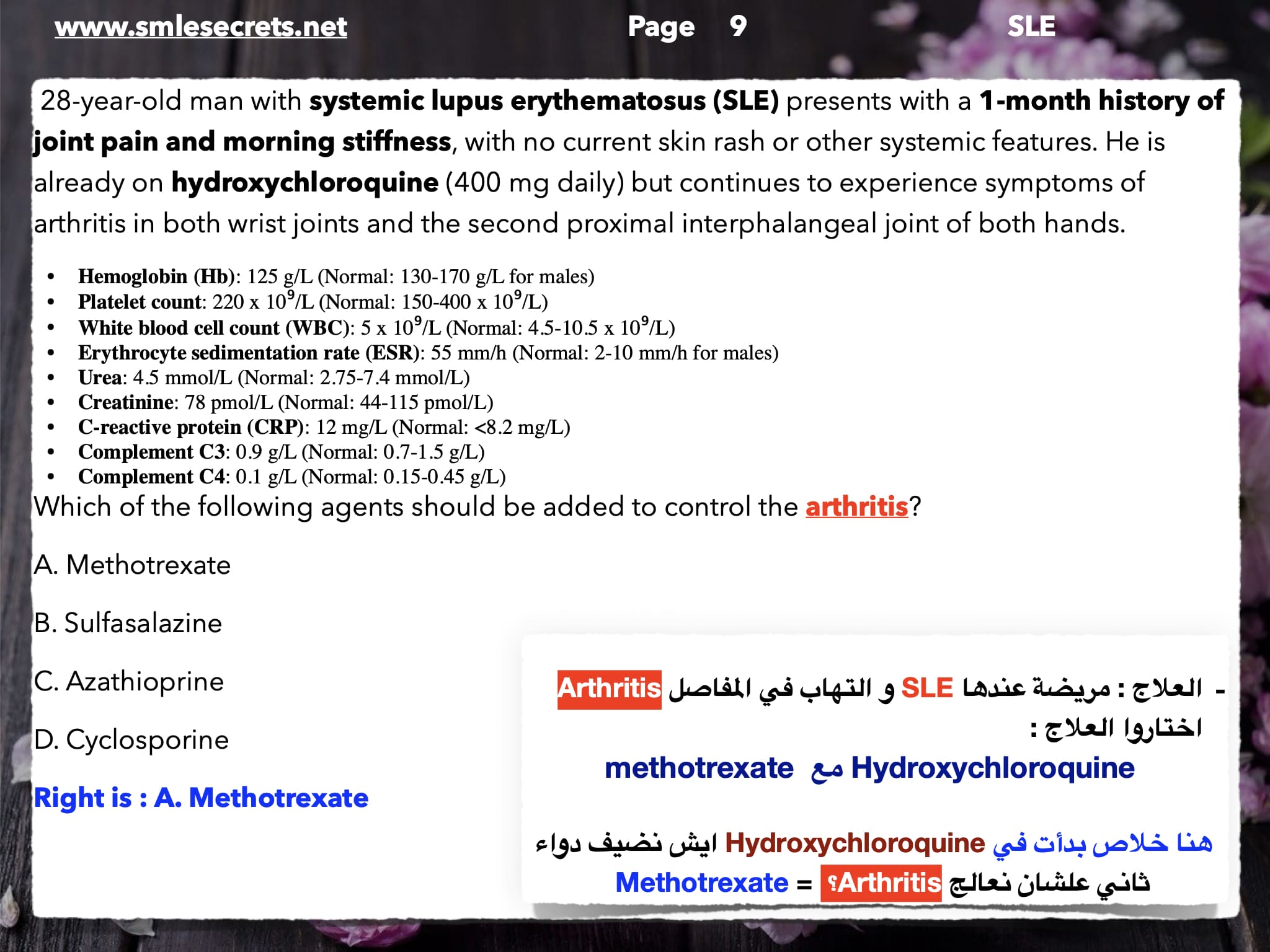
What is the treatment of skin involvement in SLE?
Answer: Hydroxychloroquine
Recall 4:
SLE patient with high anti-ribosomal antibody. What is the diagnosis?
Answer: Lupus neuritis
Recall 5:
Case of SLE with neuritis, what is the treatment?
A) Oral prednisone
B) IV Methylprednisolone – IV prednisone✔️
C) Plasmapheresis
Recall 6:
Case of SLE with anti-neural antibodies in CSF, what is the diagnosis?
Answer: Lupus encephalitis
Recall 7:
SLE with stroke, what is the treatment?
Answer: Pulse steroid + Pulse cyclophosphamide
Recall 8:
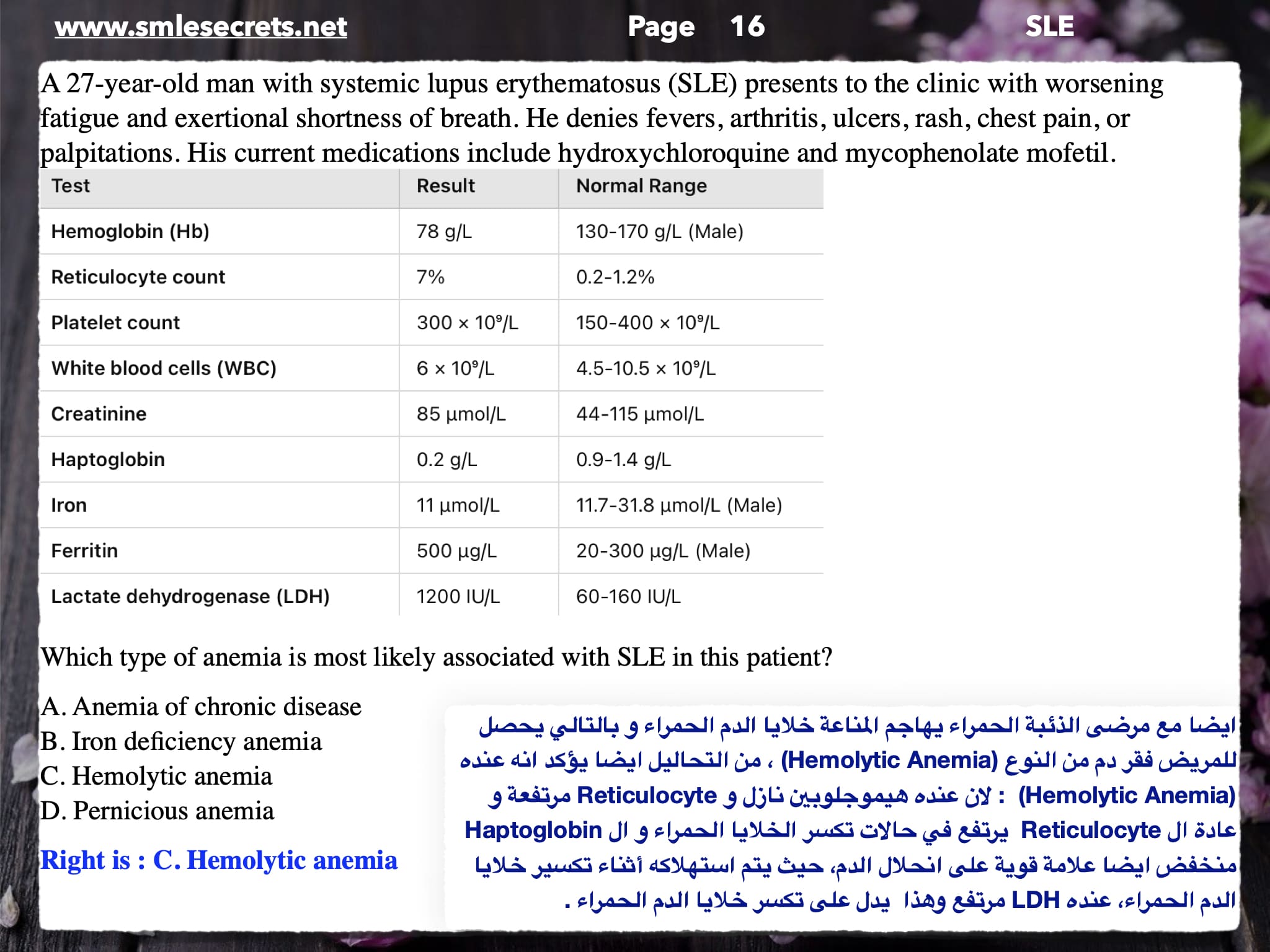
SLE + hemiparesis + high LDH + blood smear shows schistocytes. What is the treatment?
A) oral Prednisolone
B) IV Methylprednisolone ✔️
C) Plasmapheresis
Recall 9:
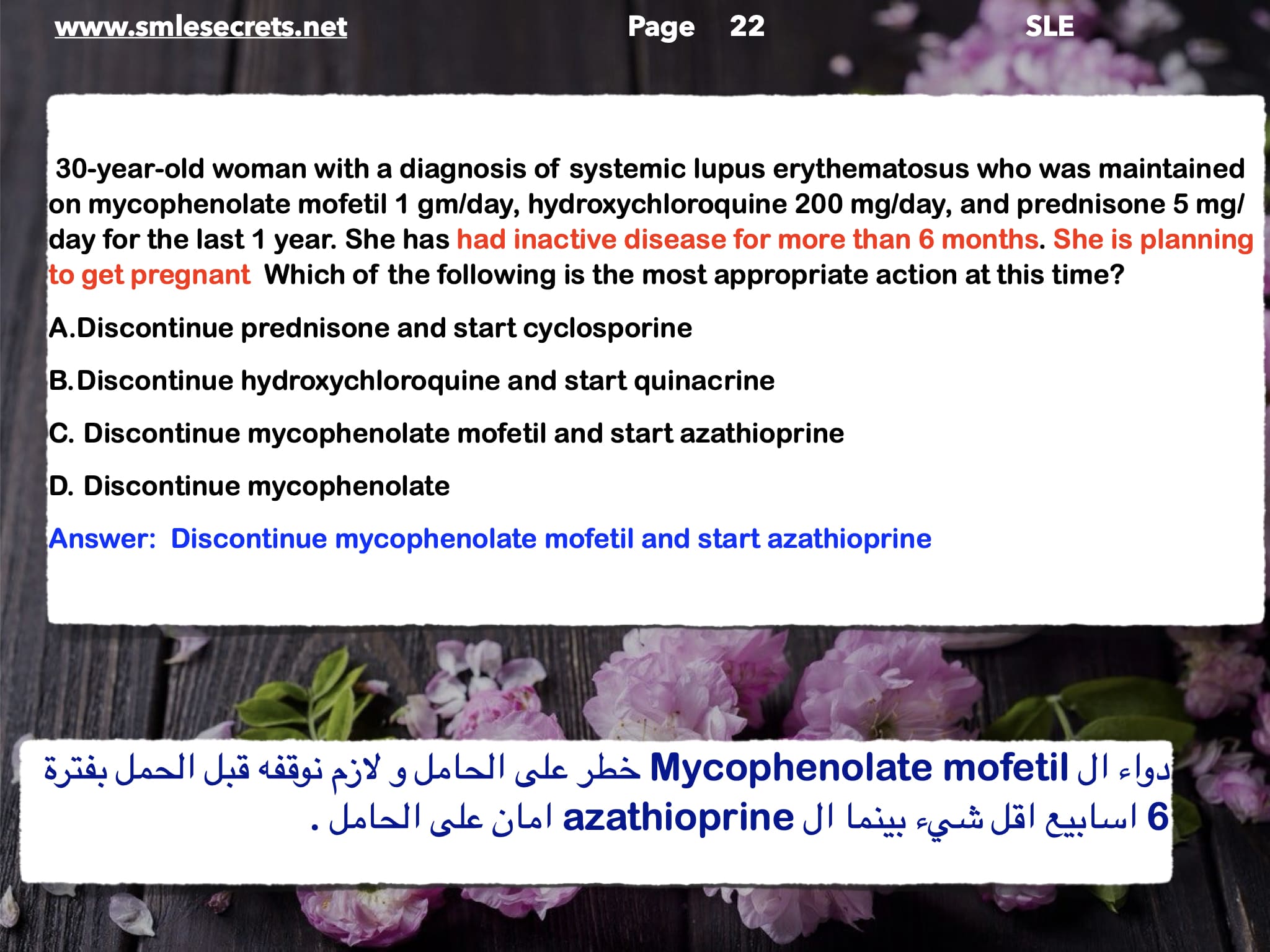
Active SLE in 24-year-old with hemiparesis, what is the treatment?
Answer: Mycophenolate?? or Prednisolone??
Recall 10:
Question: The most common CNS manifestation in SLE?
A) Headache (1st most common)
B) Psychosis / Depression (2nd most common)
C) Seizure (Not common)
Recall 11:
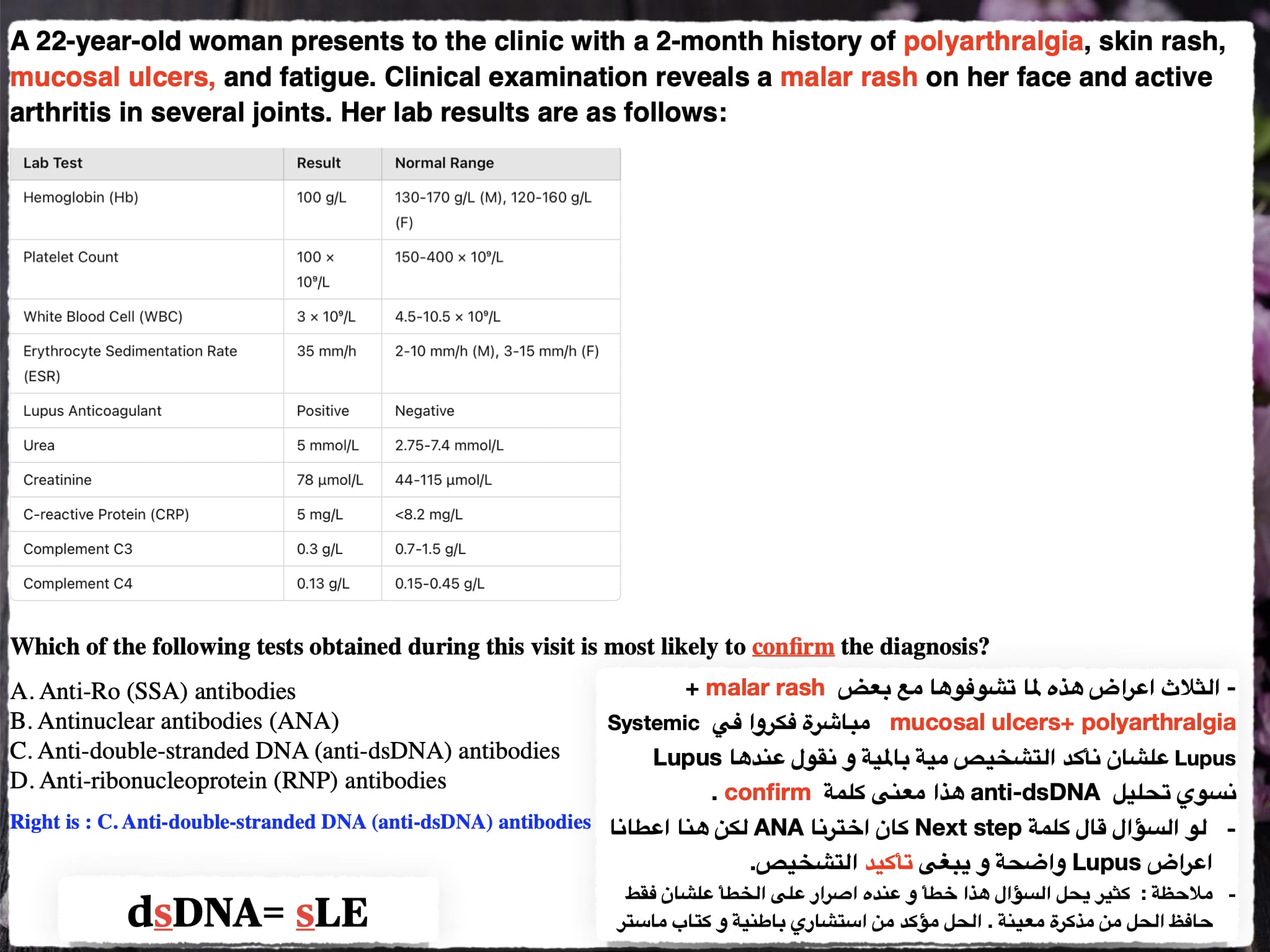
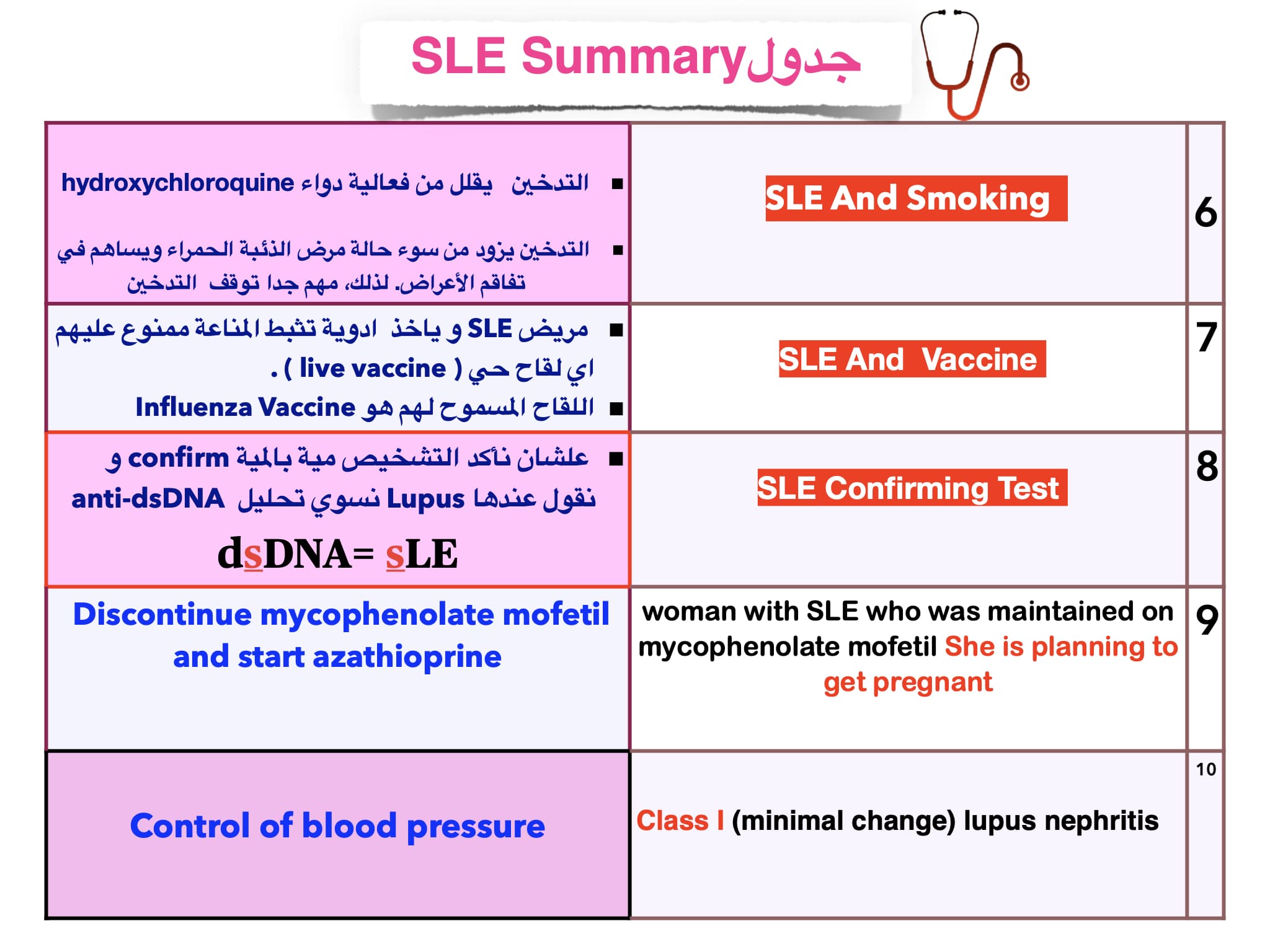
Which lab marker indicates SLE disease activity?
Answer: Anti-double-stranded DNA (dsDNA)
Recall 12:
Which drug may cause high anti-dsDNA without SLE?
A) Infliximab ✔️
B) Cyclophosphamide
C) Cyclosporin
Recall 13:
A case of SLE with proteinuria on lab results. What is the next step?
A) Start steroids
B) Start cyclophosphamide
C) Wait until renal biopsy ✔️
Recall 14:
What is the most common type of lupus nephritis?
Answer: Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis (GN)
Recall 15:
Female with lupus nephritis. Which lab value correlates most with disease activity?
A) dsDNA ✔️
B) Raised complement
Recall 16:
What is the most specific test for lupus nephritis diagnosis?
A) ANA
B) Anti-dsDNA ✔️
C) RNP
Recall 17:
SLE with suspected lupus nephritis. What should you do before treatment?
A) Start steroids
B) Start cyclophosphamide
C) Wait until renal biopsy ✔️
Recall 18:
What is the electron microscopy (EM) finding of SLE renal biopsy?
A) Mesangial
B) Membranous
C) Subendothelial
D) Diffuse GN ✔️؟
Recall 19:
SLE patient with proteinuria 3+ on dipstick. What is the treatment?
A) Prednisone✔️
B) IV Methylprednisolone
Recall 20:
SLE with lupus nephritis and proteinuria. What is the treatment plan?
Answer: Methylprednisolone pulse (3–5 days) then oral prednisone
Recall 21:
Case of SLE with proteinuria + hematuria. What is the most appropriate treatment?
Answer: Cyclophosphamide + Methylprednisolone / MMF + Methylprednisolone
Recall 22:
SLE with proteinuria (suggestive of lupus nephropathy). Next step?
Answer: Renal biopsy (GN + lupus → biopsy)
Recall 23″
Lupus nephritis classification – which is true?
A) Class 2 treated by corticosteroids
B) Class 3 treated by corticosteroids + cyclophosphamide/MMF ✔️
C) Class 4 has the worst prognosis ✔️
Recall 24:
Patient with lupus nephritis. Which of the following is correct?
A) Class 1 & 2 nephritis require no treatment
B) Class 3 is treated with aggressive therapy ✔️
C) Class 5 has poor prognosis
Recall 25:
What is the indication for chemotherapy in SLE nephropathy?
Answer: Class 3 or 4 lupus nephritis
Recall 26:
Case: Young girl with lupus + nephrotic syndrome. Treatment?
Answer: MMF + Steroid
Recall 27:
Which lupus nephritis class has worst prognosis?
Answer: Diffuse proliferative GN
Treatment: Cyclophosphamide + Steroid
Recall 28:
Case: Malar rash + photosensitivity + proteinuria (3+) + rash on face including nasal bridge. Most specific antibody?
Answer: Anti-Smith
📝 (Anti-DNA not in options)
Recall 29:
What is the most specific antibody for SLE?
Answer: Anti-Smith
📝 1st: Anti-Smith → 2nd: Anti-dsDNA
Recall 30:
Drug-induced lupus is associated with which antibody?
Answer: Anti-Histone
Recall 31:
Drug-induced lupus – Occurs with slow activity.
A) Fast onset of activity
B) Slow onset of activity ✔️
C) Rapid progression
Recall 32:
Penicillamine & Gold drug-induced GN – Occurs more in slow acetylators.
A) More common in fast acetylators
B) More common in slow acetylators ✔️
C) Not affected by acetylator status
Recall 33:
Drug-induced lupus – Occurs more in slow acetylators.
A) Occurs more in fast acetylators
B) Occurs more in slow acetylators ✔️
C) Not reversible on stopping the offending drug
Recall 34:
SLE flare during pregnancy – What is the most appropriate treatment?
A) Prednisone
B) Dexamethasone
C) Betamethasone
D) Methylprednisolone✔️؟؟؟
Recall 35:
Q- What is the most common clinical manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)?
A) Renal involvement
B) Pericarditis
C) Malar rash
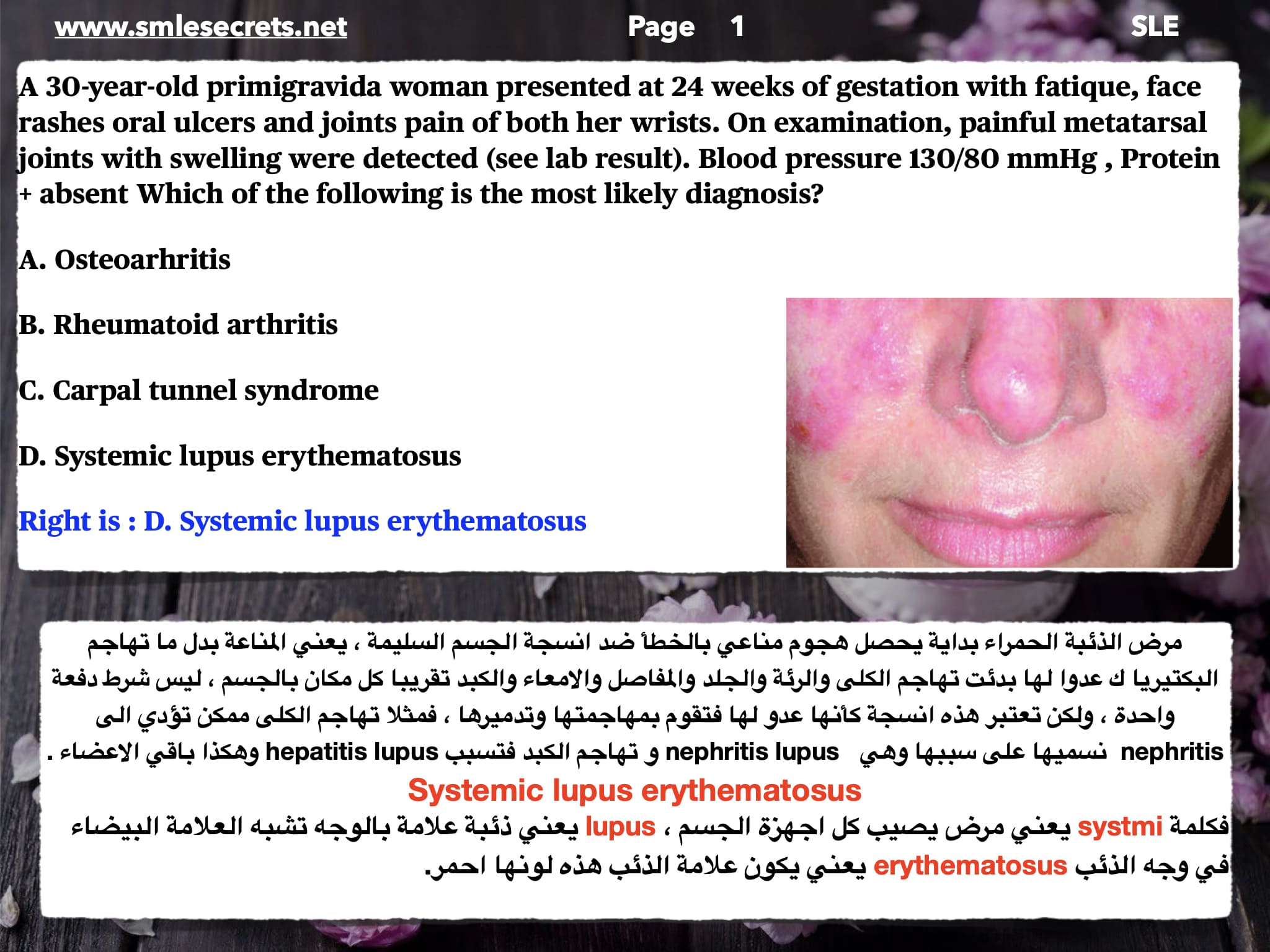
D) Arthritis ✔️
Recall 36:
What is the most specific feature of SLE?
A) Malar rash
B) Nephritis
C) Arthritis
D) Alopecia
Correct answer: Malar rash